Digital Content Flow and Life Cycle: Global E-Commerce
Posted on | February 25, 2016 | No Comments
The term “e-commerce” provokes connotations of computer users “surfing” the web and using their credit cards to make online purchases. While this has been the popular conception, e-commerce continues to transform. The traditional model will continue to drive strong e-commerce sales for the retail sector, but other technologies and business models will also be important, especially with the proliferation of mobile and social technologies. E-commerce is as dynamic as the technologies and creative impulses involved and can be expected to morph and expand in concert with new innovations.
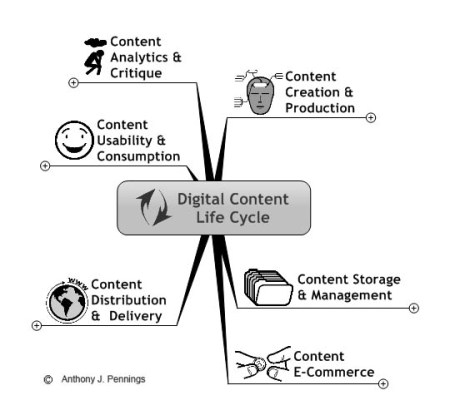
In this post, I will start to examine how e-commerce is a crucial stage in adding value to digital content. The graphic below represents the key steps in the digital media production cycle, starting at one o’clock.
The introduction of e-commerce into the media content life cycle is relatively new. I gave a talk to the Asian Business Forum in Singapore during the summer of 2000 that suggested broadcasters adopt an e-commerce model that included digitally serving, customizing, transacting, monetizing, interacting, delivering, and personalizing content.[1] I received quite a few blank stares at the time, maybe because it was a conference on “Broadcasting in the Internet Age.” Coming from New York City, I was familiar with the Silicon Alley discussions about the Internet and the changing media industries.
An analysis of the flow of digital content production can help companies determine the steps of web content globalization. A chain analysis involves diagramming then analyzing the various value-creating activities in the content production, storage, monetization, and distribution process. Furthermore, it involves an analysis of “informating” process, the stream of data that is produced in the content life cycle process. Digital content passes through a series of value-adding steps that prepare it for global deployment via data distribution channels to HDTV, mobile devices, and websites.[4]
Through this analysis, the major value-creating steps of content production and marketing process can be systematically identified and managed. In the graph above, core steps in digital production and linkages between them are identified in the context of advanced digital technologies. These are general representations but provide a framework to analyze the activities and flow of content production. Identifying these processes helps to understand the equipment, logistics, and skill sets involved in modern media production and also processes that lead to waste. In other posts I will discuss each of the following:
The Digital Value Chain
Content Creation and Production
Content Storage and Management
Content E-Commerce
Content Distribution and Delivery
Content Usability and Consumption
Content Analytics and Critique
Notes
[1] “Internet and Broadcasting: Friends or Foes?” Invited Presentation to the to the Asian Business Forum, July 07, 2000. Conference on Broadcasting in the Internet Age. Sheraton Towers, Singapore.
[2] Porter, Michael E. Competitive Advantage. 1985, Ch. 1, pp 11-15. The Free Press. New York.
[3] A version of this article appeared in the November–December 1995 issue of the Harvard Business Review.
[4] Singh, Nitish. Localization Strategies for Global E-Business.
© ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
 Anthony J. Pennings, PhD is Professor and Associate Chair of the Department of Technology and Society, State University of New York, Korea. Before joining SUNY, he taught at Hannam University in South Korea and from 2002-2012 was on the faculty of New York University. Previously, he taught at St. Edwards University in Austin, Texas, Marist College in New York, and Victoria University in New Zealand. He has also spent time as a Fellow at the East-West Center in Honolulu, Hawaii.
Anthony J. Pennings, PhD is Professor and Associate Chair of the Department of Technology and Society, State University of New York, Korea. Before joining SUNY, he taught at Hannam University in South Korea and from 2002-2012 was on the faculty of New York University. Previously, he taught at St. Edwards University in Austin, Texas, Marist College in New York, and Victoria University in New Zealand. He has also spent time as a Fellow at the East-West Center in Honolulu, Hawaii.
Tags: e-commerce > global e-commerce > value chains